Migrating from ibc-go v5 to v6
This document is intended to highlight significant changes which may require more information than presented in the CHANGELOG. Any changes that must be done by a user of ibc-go should be documented here.
There are four sections based on the four potential user groups of this document:
- Chains
- IBC Apps
- Relayers
- IBC Light Clients
Note: ibc-go supports golang semantic versioning and therefore all imports must be updated to bump the version number on major releases.
Chains
The ibc-go/v6 release introduces a new set of migrations for 27-interchain-accounts. Ownership of ICS27 channel capabilities is transferred from ICS27 authentication modules and will now reside with the ICS27 controller submodule moving forward.
For chains which contain a custom authentication module using the ICS27 controller submodule this requires a migration function to be included in the chain upgrade handler. A subsequent migration handler is run automatically, asserting the ownership of ICS27 channel capabilities has been transferred successfully.
This migration is not required for chains which do not contain a custom authentication module using the ICS27 controller submodule.
This migration facilitates the addition of the ICS27 controller submodule MsgServer which provides a standardised approach to integrating existing forms of authentication such as x/gov and x/group provided by the Cosmos SDK.
For more information please refer to ADR 009.
Upgrade proposal
Please refer to PR #2383 for integrating the ICS27 channel capability migration logic or follow the steps outlined below:
- Add the upgrade migration logic to chain distribution. This may be, for example, maintained under a package
app/upgrades/v6.
package v6
import (
"github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/codec"
storetypes "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/store/types"
sdk "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types"
"github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types/module"
capabilitykeeper "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/x/capability/keeper"
upgradetypes "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/x/upgrade/types"
v6 "github.com/cosmos/ibc-go/v6/modules/apps/27-interchain-accounts/controller/migrations/v6"
)
const (
UpgradeName = "v6"
)
func CreateUpgradeHandler(
mm *module.Manager,
configurator module.Configurator,
cdc codec.BinaryCodec,
capabilityStoreKey *storetypes.KVStoreKey,
capabilityKeeper *capabilitykeeper.Keeper,
moduleName string,
) upgradetypes.UpgradeHandler {
return func(ctx sdk.Context, _ upgradetypes.Plan, vm module.VersionMap) (module.VersionMap, error) {
if err := v6.MigrateICS27ChannelCapability(ctx, cdc, capabilityStoreKey, capabilityKeeper, moduleName); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return mm.RunMigrations(ctx, configurator, vm)
}
}
- Set the upgrade handler in
app.go. ThemoduleNameparameter refers to the authentication module'sScopedKeepername. This is the name provided upon instantiation inapp.govia thex/capabilitykeeperScopeToModule(moduleName string)method. See here for an example insimapp.
app.UpgradeKeeper.SetUpgradeHandler(
v6.UpgradeName,
v6.CreateUpgradeHandler(
app.mm,
app.configurator,
app.appCodec,
app.keys[capabilitytypes.ModuleName],
app.CapabilityKeeper,
>>>> moduleName <<<<,
),
)
IBC Apps
ICS27 - Interchain Accounts
Controller APIs
In previous releases of ibc-go, chain developers integrating the ICS27 interchain accounts controller functionality were expected to create a custom Base Application referred to as an authentication module, see the section Building an authentication module from the documentation.
The Base Application was intended to be composed with the ICS27 controller submodule Keeper and facilitate many forms of message authentication depending on a chain's particular use case.
Prior to ibc-go v6 the controller submodule exposed only these two functions (to which we will refer as the legacy APIs):
However, these functions have now been deprecated in favour of the new controller submodule MsgServer and will be removed in later releases.
Both APIs remain functional and maintain backwards compatibility in ibc-go v6, however consumers of these APIs are now recommended to follow the message passing paradigm outlined in Cosmos SDK ADR 031 and ADR 033. This is facilitated by the Cosmos SDK MsgServiceRouter and chain developers creating custom application logic can now omit the ICS27 controller submodule Keeper from their module and instead depend on message routing.
Depending on the use case, developers of custom authentication modules face one of three scenarios:
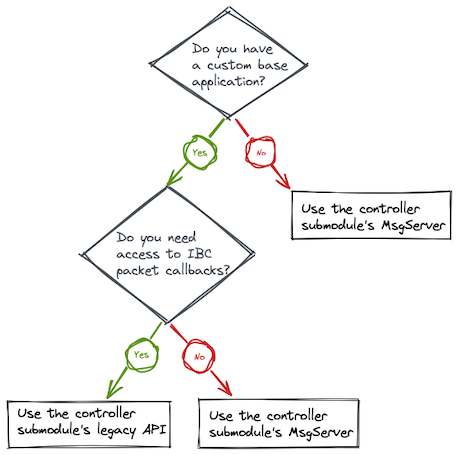
My authentication module needs to access IBC packet callbacks
Application developers that wish to consume IBC packet callbacks and react upon packet acknowledgements must continue using the controller submodule's legacy APIs. The authentication modules will not need a ScopedKeeper anymore, though, because the channel capability will be claimed by the controller submodule. For example, given an Interchain Accounts authentication module keeper ICAAuthKeeper, the authentication module's ScopedKeeper (scopedICAAuthKeeper) is not needed anymore and can be removed for the argument list of the keeper constructor function, as shown here:
app.ICAAuthKeeper = icaauthkeeper.NewKeeper(
appCodec,
keys[icaauthtypes.StoreKey],
app.ICAControllerKeeper,
- scopedICAAuthKeeper,
)
Please note that the authentication module's ScopedKeeper name is still needed as part of the channel capability migration described in section Upgrade proposal above. Therefore the authentication module's ScopedKeeper cannot be completely removed from the chain code until the migration has run.
In the future, the use of the legacy APIs for accessing packet callbacks will be replaced by IBC Actor Callbacks (see ADR 008 for more details) and it will also be possible to access them with the MsgServiceRouter.
My authentication module does not need access to IBC packet callbacks
The authentication module can migrate from using the legacy APIs and it can be composed instead with the MsgServiceRouter, so that the authentication module is able to pass messages to the controller submodule's MsgServer to register interchain accounts and send packets to the interchain account. For example, given an Interchain Accounts authentication module keeper ICAAuthKeeper, the ICS27 controller submodule keeper (ICAControllerKeeper) and authentication module scoped keeper (scopedICAAuthKeeper) are not needed anymore and can be replaced with the MsgServiceRouter, as shown here:
app.ICAAuthKeeper = icaauthkeeper.NewKeeper(
appCodec,
keys[icaauthtypes.StoreKey],
- app.ICAControllerKeeper,
- scopedICAAuthKeeper,
+ app.MsgServiceRouter(),
)
In your authentication module you can route messages to the controller submodule's MsgServer instead of using the legacy APIs. For example, for registering an interchain account:
- if err := keeper.icaControllerKeeper.RegisterInterchainAccount(
- ctx,
- connectionID,
- owner.String(),
- version,
- ); err != nil {
- return err
- }
+ msg := controllertypes.NewMsgRegisterInterchainAccount(
+ connectionID,
+ owner.String(),
+ version,
+ )
+ handler := keeper.msgRouter.Handler(msg)
+ res, err := handler(ctx, msg)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
where controllertypes is an import alias for "github.com/cosmos/ibc-go/v6/modules/apps/27-interchain-accounts/controller/types".
In addition, in this use case the authentication module does not need to implement the IBCModule interface anymore.
I do not need a custom authentication module anymore
If your authentication module does not have any extra functionality compared to the default authentication module added in ibc-go v6 (the MsgServer), or if you can use a generic authentication module, such as the x/auth, x/gov or x/group modules from the Cosmos SDK (v0.46 and later), then you can remove your authentication module completely and use instead the gRPC endpoints of the MsgServer or the CLI added in ibc-go v6.
Please remember that the authentication module's ScopedKeeper name is still needed as part of the channel capability migration described in section Upgrade proposal above.
Host params
The ICS27 host submodule default params have been updated to include the AllowAllHostMsgs wildcard *.
This enables execution of any sdk.Msg type for ICS27 registered on the host chain InterfaceRegistry.
// AllowAllHostMsgs holds the string key that allows all message types on interchain accounts host module
const AllowAllHostMsgs = "*"
...
// DefaultParams is the default parameter configuration for the host submodule
func DefaultParams() Params {
- return NewParams(DefaultHostEnabled, nil)
+ return NewParams(DefaultHostEnabled, []string{AllowAllHostMsgs})
}
API breaking changes
SerializeCosmosTx takes in a []proto.Message instead of []sdk.Message. This allows for the serialization of proto messages without requiring the fulfillment of the sdk.Msg interface.
The 27-interchain-accounts genesis types have been moved to their own package: modules/apps/27-interchain-accounts/genesis/types.
This change facilitates the addition of the ICS27 controller submodule MsgServer and avoids cyclic imports. This should have minimal disruption to chain developers integrating 27-interchain-accounts.
The ICS27 host submodule NewKeeper function in modules/apps/27-interchain-accounts/host/keeper now includes an additional parameter of type ICS4Wrapper.
This provides the host submodule with the ability to correctly unwrap channel versions in the event of a channel reopening handshake.
func NewKeeper(
cdc codec.BinaryCodec, key storetypes.StoreKey, paramSpace paramtypes.Subspace,
- channelKeeper icatypes.ChannelKeeper, portKeeper icatypes.PortKeeper,
+ ics4Wrapper icatypes.ICS4Wrapper, channelKeeper icatypes.ChannelKeeper, portKeeper icatypes.PortKeeper,
accountKeeper icatypes.AccountKeeper, scopedKeeper icatypes.ScopedKeeper, msgRouter icatypes.MessageRouter,
) Keeper
ICS29 - NewKeeper API change
The NewKeeper function of ICS29 has been updated to remove the paramSpace parameter as it was unused.
func NewKeeper(
- cdc codec.BinaryCodec, key storetypes.StoreKey, paramSpace paramtypes.Subspace,
- ics4Wrapper types.ICS4Wrapper, channelKeeper types.ChannelKeeper, portKeeper types.PortKeeper, authKeeper types.AccountKeeper, bankKeeper types.BankKeeper,
+ cdc codec.BinaryCodec, key storetypes.StoreKey,
+ ics4Wrapper types.ICS4Wrapper, channelKeeper types.ChannelKeeper,
+ portKeeper types.PortKeeper, authKeeper types.AccountKeeper, bankKeeper types.BankKeeper,
) Keeper {
ICS20 - SendTransfer is no longer exported
The SendTransfer function of ICS20 has been removed. IBC transfers should now be initiated with MsgTransfer and routed to the ICS20 MsgServer.
See below for example:
if handler := msgRouter.Handler(msgTransfer); handler != nil {
if err := msgTransfer.ValidateBasic(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
res, err := handler(ctx, msgTransfer)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
ICS04 - SendPacket API change
The SendPacket API has been simplified:
// SendPacket is called by a module in order to send an IBC packet on a channel
func (k Keeper) SendPacket(
ctx sdk.Context,
channelCap *capabilitytypes.Capability,
- packet exported.PacketI,
-) error {
+ sourcePort string,
+ sourceChannel string,
+ timeoutHeight clienttypes.Height,
+ timeoutTimestamp uint64,
+ data []byte,
+) (uint64, error) {
Callers no longer need to pass in a pre-constructed packet.
The destination port/channel identifiers and the packet sequence will be determined by core IBC.
SendPacket will return the packet sequence.
IBC testing package
The SendPacket API has been simplified:
// SendPacket is called by a module in order to send an IBC packet on a channel
func (k Keeper) SendPacket(
ctx sdk.Context,
channelCap *capabilitytypes.Capability,
- packet exported.PacketI,
-) error {
+ sourcePort string,
+ sourceChannel string,
+ timeoutHeight clienttypes.Height,
+ timeoutTimestamp uint64,
+ data []byte,
+) (uint64, error) {
Callers no longer need to pass in a pre-constructed packet. SendPacket will return the packet sequence.
Relayers
- No relevant changes were made in this release.
IBC Light Clients
- No relevant changes were made in this release.